Red clover is known both as a cover crop and forage crop and is available in many regions, such as the northeast, mid-Atlantic, and midwest areas. Depending on what you use it for, the seeding time for red clover will differ.
But generally speaking, people often seed this plant in late summer and early fall (around August to November) to improve the soil. To provide grazing for animals, farmers will instead throw and grow clover seeds in spring after the last frost, around March or April. Read below for more information on when to plant red clover.
Table of Contents
Overview of Red Clover
| Name | Trifolium pratense |
| Appearance | Eight to thirty-one inches tall with trifoliate leaves and dark pink flowers |
| Hardiness zones | Zone 3 to zone 9a. In places higher than zone 8, it is an annual. |
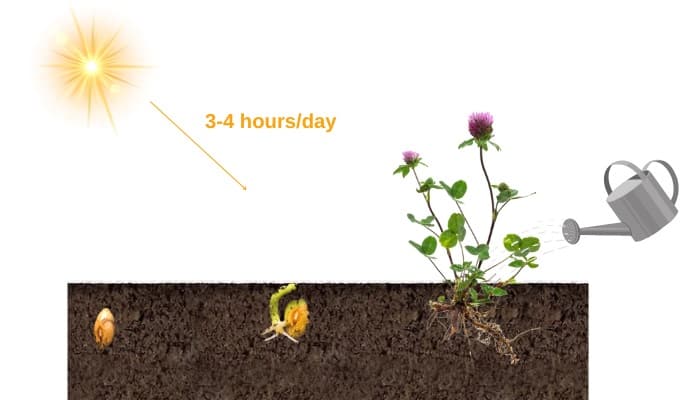
| Watering | Whenever the soil feels dry |
| Soil requirements | 6.0 to 8.0 for health, or 6.2 to 6.5 for high yields |
| Germination temperature | 41 to 59℉ |
Best Time to Plant Red Clover
The ideal red clover planting time is the one we mentioned in the intro—or, to repeat, late summer and early fall for cover crop establishment and after the last frost in spring for red clover used as forage.
However, you will also find people planting red clover outside of these periods, namely in early summer and late winter.
- In early summer or late June, people tend to grow clover with corn and soybeans to regulate nitrogen in the soil and suppress weeds. Often, they do this six weeks after a herbicide application.
- In a similar fashion, winter seeding or frost seeding of red clover with wheat and barley (i.e. dormant winter grains) occurs when the snow starts to melt but has not disappeared entirely.
In other words, people plant red clover seed as a cover crop when temperatures start to fluctuate between above freezing and below freezing.
These environmental changes help push the seeds into the soil and allow for eventual germination, provided you thin the grain straws down enough so that they won’t suppress the clover.
With that out of the way, here’s a summary of the planting time for red clover:
- February to April for winter frost-seeding
- Spring planting in March to April for forage in the summer or fall
- Interseeding with corn and soybeans in late June
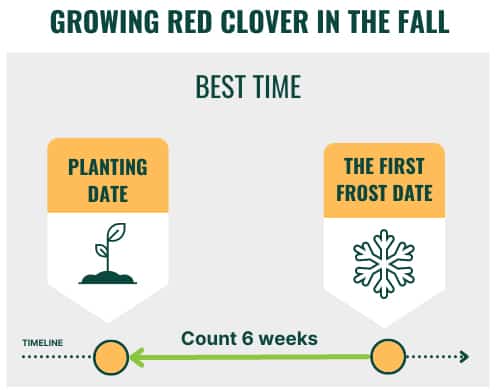
- Plant in the fall or late summer as a cover crop, at least six weeks before the first frost. This would be around August or September in the north and in October or September in the south. These months are also the best time to plant clover for deer.
Red Clover Varieties
Red clover is classifiable into two types: early-flowering or medium red clover and late-flowering or mammoth red clover. Medium clover varieties produce more hay than mammoth types (up to three crops versus one crop per year), but mammoth cultivars are taller and more suitable for dry environments.
Mammoth varieties are also preferable if you only need supplemental biomass and nitrogen in one growing season, since the cost of medium clover seeds needs to be offset over multiple cuttings to make them worth it.
Medium red clover includes varieties like Midland, Kenland, Kenstar, Pennscott, Cumberland, Lakeland, Dollard, Chesapeake, and Renegade Red. These are more common in the US than mammoth varieties such as Norlac and Craig.
How to Plant Red Clover
On the planting dates, check your soil and avoid areas that are soggy or wet from rain. Till the ground to remove weeds and inoculate the seeds with Rhizobium bacteria if necessary. However, I recommend buying pre-inoculated seeds so that you have one less thing to do.
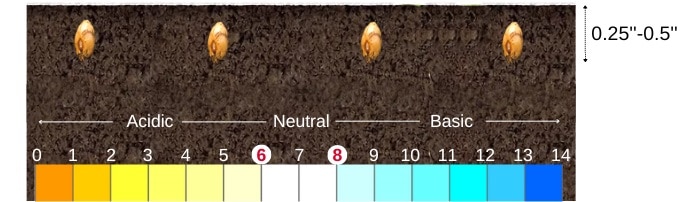
Once the preparation’s ready, plant red clover in well-drained soil with a pH of 6.0 to 8.0, or aim for a range of 6.2 to 6.5 if you’re after high yields.
Note that the seeding rates can vary, depending on whether you’re mixing or planting clover with other crops, your location, plus methods of sowing (broadcast seeding, drilling, or cultipacker, to name a few).
You can overseed and mix red clover with many crops, but we’ll focus on grass here, given that the two make great pastures for grazing animals.
Before sowing, mix your clover and grass seeds in a 1:1 ratio. Plant clover seeds at a depth of ¼ to ½ inch at a rate of about 10 pounds per acre or whatever your variety recommends as the seeding rate for red clover. Don’t be tempted to push the seeds deeper into the soil, or germination time may never come.
It’ll take around a week for sprouting to occur, provided the temperature ranges from 41 to 59℉, but you don’t have to worry if you winter-seeded clover, considering the seeds can survive freezing weather.
Care and Maintenance Tips
Red clover characteristics allow it to grow under both full sun and partial shade, so there’s no need for you to fuss about its sunlight requirements—three to four hours of direct sunshine per day should suffice. Watering when the soil is dry, however, is more important.
Check the planting area every day or every few days and irrigate it in the morning so that the ground has time to dry before evening comes. This practice minimizes chances of fungal disease, especially if you avoid wetting the flower heads or leaves when caring for the red clover.
You may also fertilize the soil after planting, but as with most crops, the formula to use depends on your garden’s condition. Conduct a soil test, or use 20 pounds of nitrogen with twice as much potash and three times as much phosphate.
Note that nitrogen is unnecessary when you’re seeding red clover with grass or when the red clover has become established.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of red clover?
If you’re unsure whether to plant red clover, here are some benefits to help you decide:
- Red clover adds nitrogen to the soil and suppresses weeds.
- It can function as a manure to reduce soil erosion.
- Farmers can feed red clover to cattle and use it to produce hay and silage.
- You can eat red clover flowers and leaves and treat them like a vegetable.
How long does it take for red clover to grow?
It takes sixty to seventy days for red clover to become harvestable, so you can plant and harvest red clover for deer, cows, and turkeys in a very short time. White, crimson, and ladino are other types of clover for deer worth considering.
Does red clover come back every year?
Is red clover annual or perennial? Red clover is actually a perennial. Don’t mistake it for crimson clover, as despite the two having similar names, crimson clover is an annual plant that’s hardy to zone 6 and not zone 4 like red clover.
You will see red clover reseed itself and come back for up to three years if you live in northern states. However, in the south, such as areas like Florida, southern Georgia, and southern Mississippi, it functions as an annual.
Is red clover easy to grow?
Yes. Red clover is straightforward to plant. Just avoid areas with a lot of weeds and purchase disease-resistant varieties for the best chances at growing them. If you want to, you can also try growing clover indoors as a houseplant.
Simply use a well-drained potting mix and keep the soil moist, plus follow the same seeding depth as the one you use for in-ground planting.
Conclusion
Despite being the representative flower of Vermont, red clover doesn’t just grow in the state’s zone 3 to 5 but also in hotter areas like zone 6, zone 7, or 9 of the United States. As long as you know when to plant red clover, you can enjoy the benefits of this herb, whether you use it as a cover crop, livestock feed, or homegrown vegetable.
Best time for planting other flowers:

Hi, I am William – Floridayards’ digital content creator. My job is to find answers to all your concerns with thorough research and our team’s expert advice. I will also bring you honest reviews on the best products and equipment for raising your beautiful garden. Please look forward to our work!